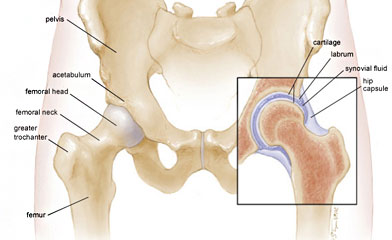
On the upper side of the pelvis (hip) bone is the acetabulum, or socket, of the ball-in-socket joint. The surface of the acetabulum is the only part of the pelvis replaced in either hip replacement or resurfacing.
The femur, or thigh bone, is the longest bone in the body. The femoral head is the ball in the ball-in-socket joint, and fits into the acetabulum. It sits on top of the femoral neck. In hip replacement surgery, the femoral neck is cut and the head is completely removed. At the base of the neck is the greater trochanter, which marks the widest point of the hip area in the skeleton.
Cartilage is a tough, elastic, gel-like layer that lines the hip joint. It is the natural bearing surface in all joints. Cartilage absorbs the shock of impact and walking, and reduces the friction in the joint to allow smooth, pain-free movement. Once injured, cartilage in adults does not heal. With enough injury, progressive deterioration can result in a worn out (arthritic) joint. It can sometimes tear, leading to joint instability and pain.
The labrum is a ring of fibrocartilage that circles the rim of the acetabulum, deepening the socket. It adds strength to the joint, but limits the range of motion.
Synovial fluid is a transparent fluid that lubricates the hip joint, much like grease in mechanical, non-living joints.
The hip capsule is made up of multiple ligaments that completely enclose the hip joint, adding to its stability.